


FINGERCLOUD
(ACCESS SERVICE PRODUCTION SUITE)
FingerCloud (Access Service Production Suite) is a modular platform of applications for the production workflow management and the production of all the access services that are required in the broadcaster’s TV and radio programmes.
The suite offers full range of access services for immersive and non–immersive media including SDH subtitle (Subtitles for the Deaf and Hard of hearing), open subtitles, spoken subtitles, audio description and sign language.
The environment is user-friendly and totally cloud-based. The applications available on this suite are designed specifically for professional users such as broadcasters who wish to offer full access services to their audience.
![]()
If you are a first-time user, click the following button to view documentation:
Click the following button to access the suite via a demo session or a permanent account:
Accessibility Content Manager (ACM)
The Accessibility Content Manager (ACM) application is a centralised management and processing system for access services such as SDH subtitles, open subtitles, spoken subtitles, audio description and sign language.
The application consists of the following components:
• ACM User Interfaces.
• ACM Engines for automatic background processes (click the “Engines tab”).
• ACM Web-Services and Interconnections with the broadcaster’s systems (click the “Web-Services and Interconnections” tab).
The ACM User Interfaces are the following:
- SM (System Management interface): Interface for administrative, configuration and maintenance issues related to the suite functionality and users coordination.
 RM (Resources Management interface): Interface for service providers administrative purposes such as work contracts, documents, skills, languages, costs, availability and other metadata so automatic or manual production tasks can be assigned to the service providers. Also to set the delivery rules and report the production volume performed by each service provider.
RM (Resources Management interface): Interface for service providers administrative purposes such as work contracts, documents, skills, languages, costs, availability and other metadata so automatic or manual production tasks can be assigned to the service providers. Also to set the delivery rules and report the production volume performed by each service provider.
- CM (Content Management interface): Most significant ACM interface aimed to different goals:
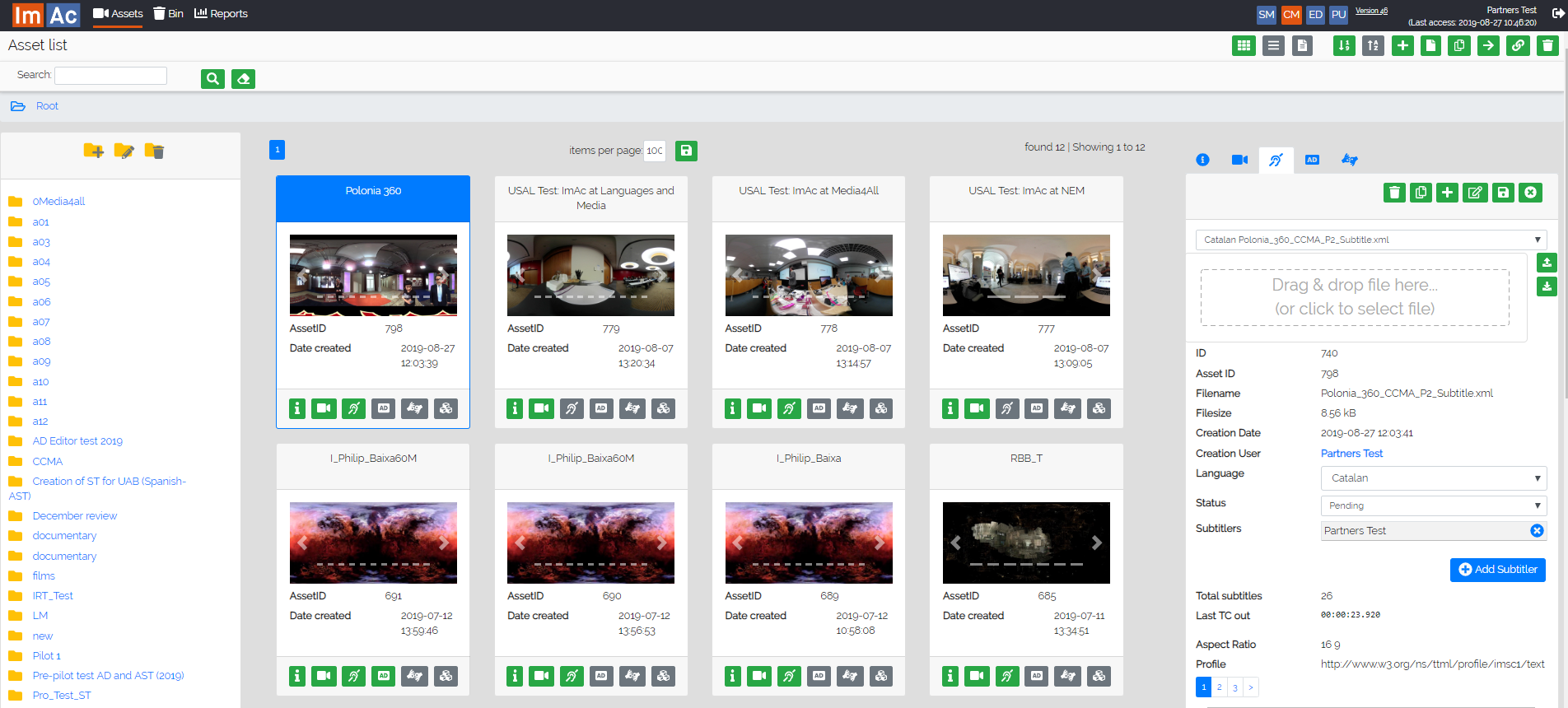
- Content library where all the access service files are available both for the user and for the broadcaster’s systems. The archive is done by means of assets, which correspond to either a television or a radio programme, with the programme metadata, files required during the production workflow such as the low quality (LQ) video/audio and all its access service files and metadata. The assets are organized in a folder tree structure for hierarchical cataloguing. Each access service instance of the asset has all its related information such as the access service file, metadata such as language(s), production due date and status, and first airing. The user can export/import each access service in multiple formats.
- Access service production workflow management through the multiple steps such as orders, ingest (video or audio file, support files and metadata), production assignment (to one or multiple producers), LQ video/audio and data delivery to producers, access service files reception, quality assurance (QA) and archive.
- Access service production status and warnings by means of the access service instance view and its filters.
- Access service production status (location in the production workflow) and warnings (if due date is approaching) by appropriate filters
- Statistics on access services filtered by dates, access service type (open subtitels, SDH subtitles, spoken subtitles, audio description, sign language), language, programme type (pre-recorded, live), etc.
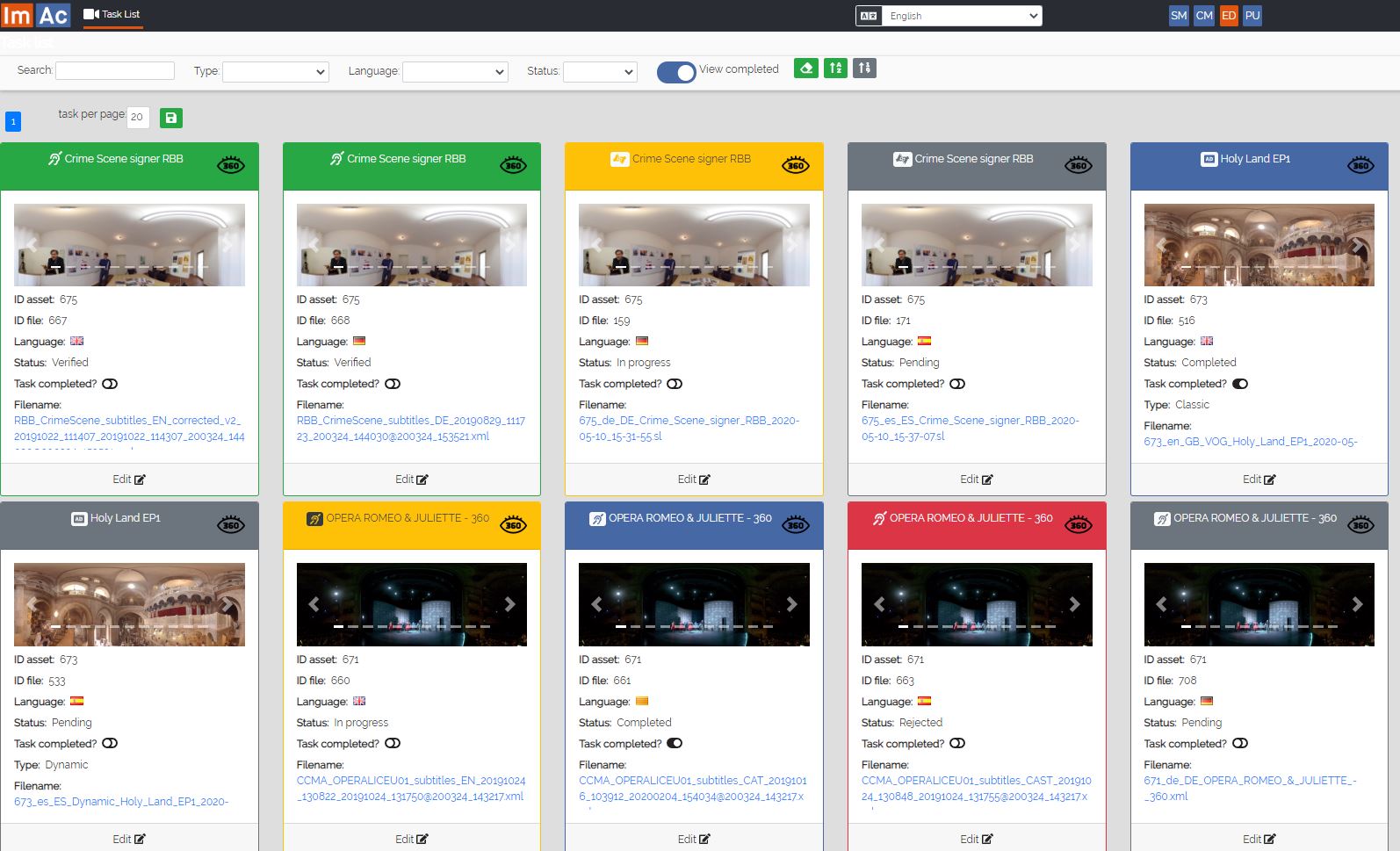 ED (EDitor interface): Interface for the access service producers (service providers or freelancers) so they can access their production tasks (jobs that have been assigned to them). This interface is totally integrated with the online editors
ED (EDitor interface): Interface for the access service producers (service providers or freelancers) so they can access their production tasks (jobs that have been assigned to them). This interface is totally integrated with the online editors
- PU (PUblication interface): Interface for the status and control of the access service publications both for linear TV channels and for other media channels such as video onDemand and social media. This interface is also used to set the publication rules for each distribution channel such as the access services and how the access service files are generated according to the channel’s technological limitations.
Access service formats:
Main used access services file formats for Broadcasters are exportable and importable via CM interface.
- Subtitle: EBU N19 .STL, .SBM, .PAC, .RAC, .890, .SRT, WebVTT, TTML (IMSC), EBU-TT(D), .SBT
- Audio description: .NAR, .AD, ADPT (TTML2), ESEF, .BWAV, WebVTT, audio track
- Sign Language: TTML-based format
Documentaion:
Some of the available ACM engines for the automatic background processes that are required during the production workflow (the engine queues and status can be monitored in the SM interface) are:
- Transcoding engine for the generation and upload LQ video to the ACM, compressed audio and image files that are required for the production workflow and archive.
- Tasks engine to automatically assign production tasks to producers when there are a straight match.
- QA engine to automatically detect warning situations in the production workflow.
- Notification engine to inform the producers and other stakeholders.
- AD Mixing engine when an audio description is validated and a mixed audio description track is required.
- Publication engine that exports the access service files according to the publication rules of each distribution channel, either linear TV channels or other media channels such as video onDemand and social media.
- Billing engine to trigger the automatic billing process for service providers according to their information and production volume.
ACM has JSON-based web-services with secured OAUTH2 authentication for external system’s queries.
ACM will also interconnect with the Broadcaster’s systems (the events of each interconnection can be monitored in the SM interface) such as:
- Ticketing System to receive access service orders automatically. When the asset with the programme ID doesn’t exist on ACM, a new radio or television asset is created with the ID. If the access service instance doesn’t exist in the asset, a new one is created. The order is added to the access service instance
- MAM to receive media for the new assets on ACM. The received media is automatically transcoded to LQ video files or compressed audio files by the Transcoding engine (see ACM engines), which are uploaded to the ACM for the production workflow
- Fingertext for the access service playout and insertion in the linear TV channels.
- Other publication systems for linear TV, internet media and socila media.
- ERP system for billing and others.
Different stakeholders will benefit from the use of ACM such as:
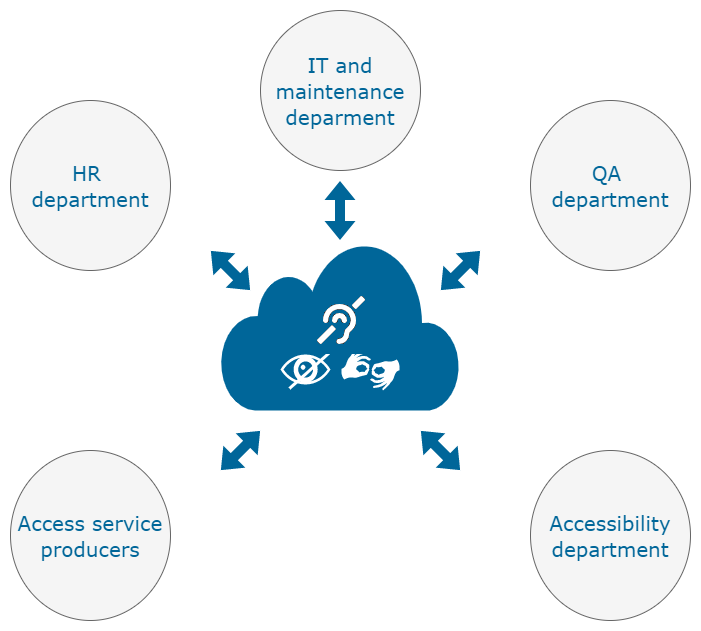
- IT and maintenance departments, may use ACM via SM for:
- Configuring the system settings, templates and engines
- Users and profiles creation, configuration and management
- Handling errors and incidences by reviewing system logs and engine status
- Accessing the engine job queues and their status
- HR deparment, may use ACM via RM for:
- Administration of producers (service providers or freelancers) based on their qualifications (languages, skills, etc.).
- Accessibility department, may use ACM via CM for:
- Creation/edition of assets (see Interfaces), which can be either manual or automatic (see interconnections)
- Creation of access service files (manual or automatic)
- Workflow management of access service file production after access service file creation and assignment to producers
- Access service producers (service providers and freelancers), may use ACM via ED for:
- Viewing assigned access service tasks and navigate through them
- Accessing to the integrated Online Editors via assigned tasks and complete them
- Changing the task status to “Completed” when the work is finished
- Viewing feedback and comments coming from broadcaster on “Rejected” tasks and take action accordingly
- QA department, may use ACM via CM for:
- Listing the access service files pending validation
- Using the integrated Online Editor to verify the access service files that are pending validation. If the quality is not right, the QA Team returns the corresponding production tasks back to the producers with the “Rejected” status and feedback information
- Validating the access service files when the quality is right for airing or publication. External systems can only get the access service files if they have been validated, although users with the right permission can access to all the access service files using the different views of the CM interface
- Statistics and reports
Online Editors
A cloud-based editor to create, edit and verify subtitle files for access services such as SDH (Subtitles for the Deaf or Hard-of-Hearing), open subtitles and spoken subtitles with a user-friendly interface and graphical video soundwave in time alongside hyper-personalised user preferences. This module is totally integrated and inter-connected to ACM.
Main features: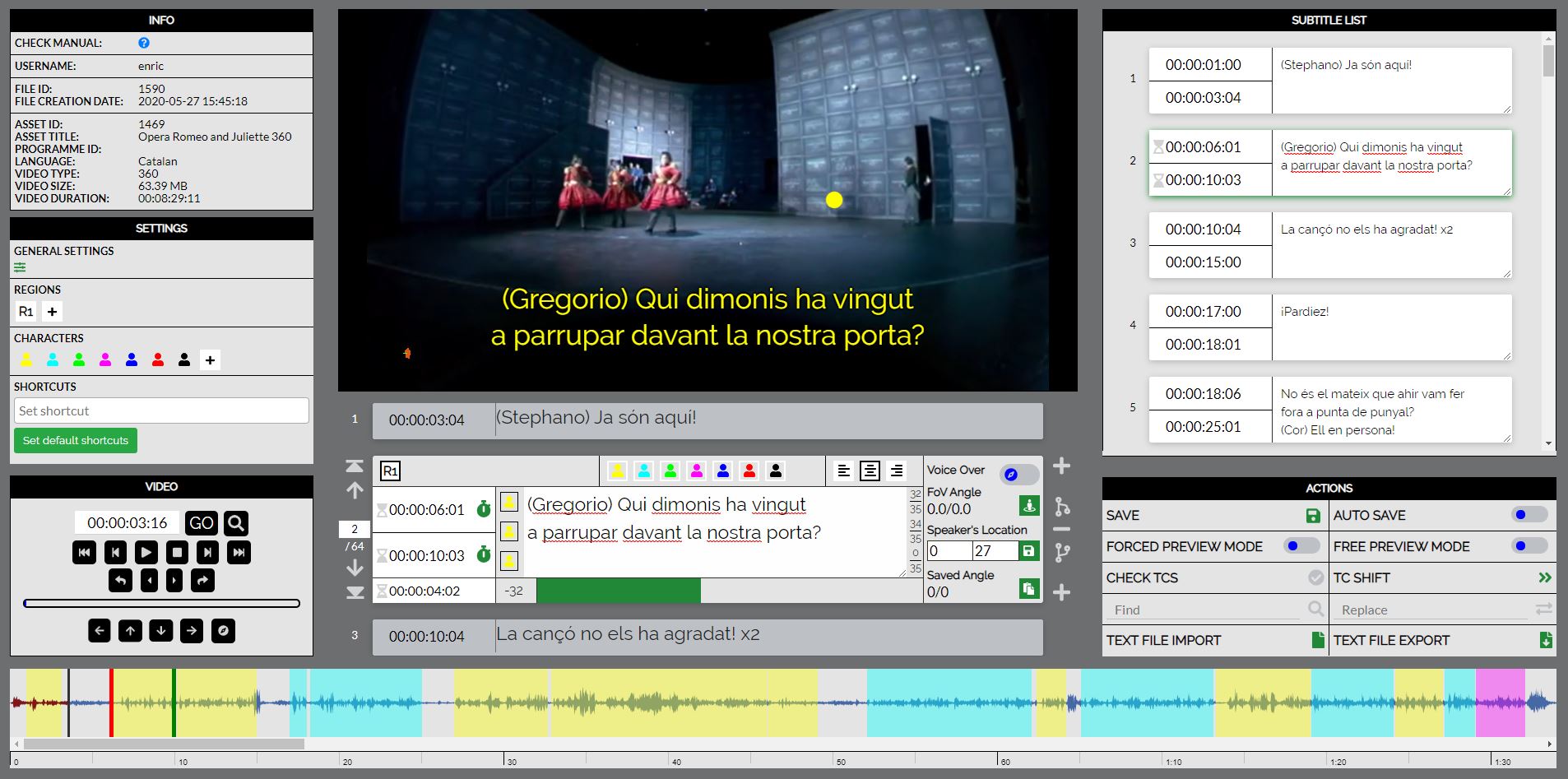
- Multi-language interface
- Standard and user-configurable shortcut keys for commonly used operations of the editor
- User and file settings (layout, preferences, languages, character configurations, region configurations, minimum values, default values, etc.). Setting profiles can be created for different programmes such as films, series, documentaries, etc. The setting profiles can be shared among producers
- Format import/export directly inside editor environment
- Character for SDH subtitles to distinguish the subtitles of each speaker. The characters are highly configurable and easy to switch between them.
- Up to 3 characters per subtitle
- Position of subtitles in regions
- Special subtitle tools required by professional users such as batch edition, insert/join/split subtitles, etc.
- Compatible with 2D and 360º (immersive) videos
- Integrity check for warnings and errors on quality constrictions
- On-screen display of full script and time codes for easy navigation
- Graphical aids such as thermometers, timeline with audio waveform and subtitle drag tools
- Preview modes for final verification purposes. 360º videos can be previewed via Specific HMD models
- IMSC-based subtitle file with all the metadata required for different formats and for production
Documentation:
The Web AD Editor is a cloud-based editor to create/edit audio description files for TV, radio and online media with a user-friendly interface and graphical video soundwave in time alongside hyper-personalized user preferences. This module is totally integrated with the ACM.
Main features:
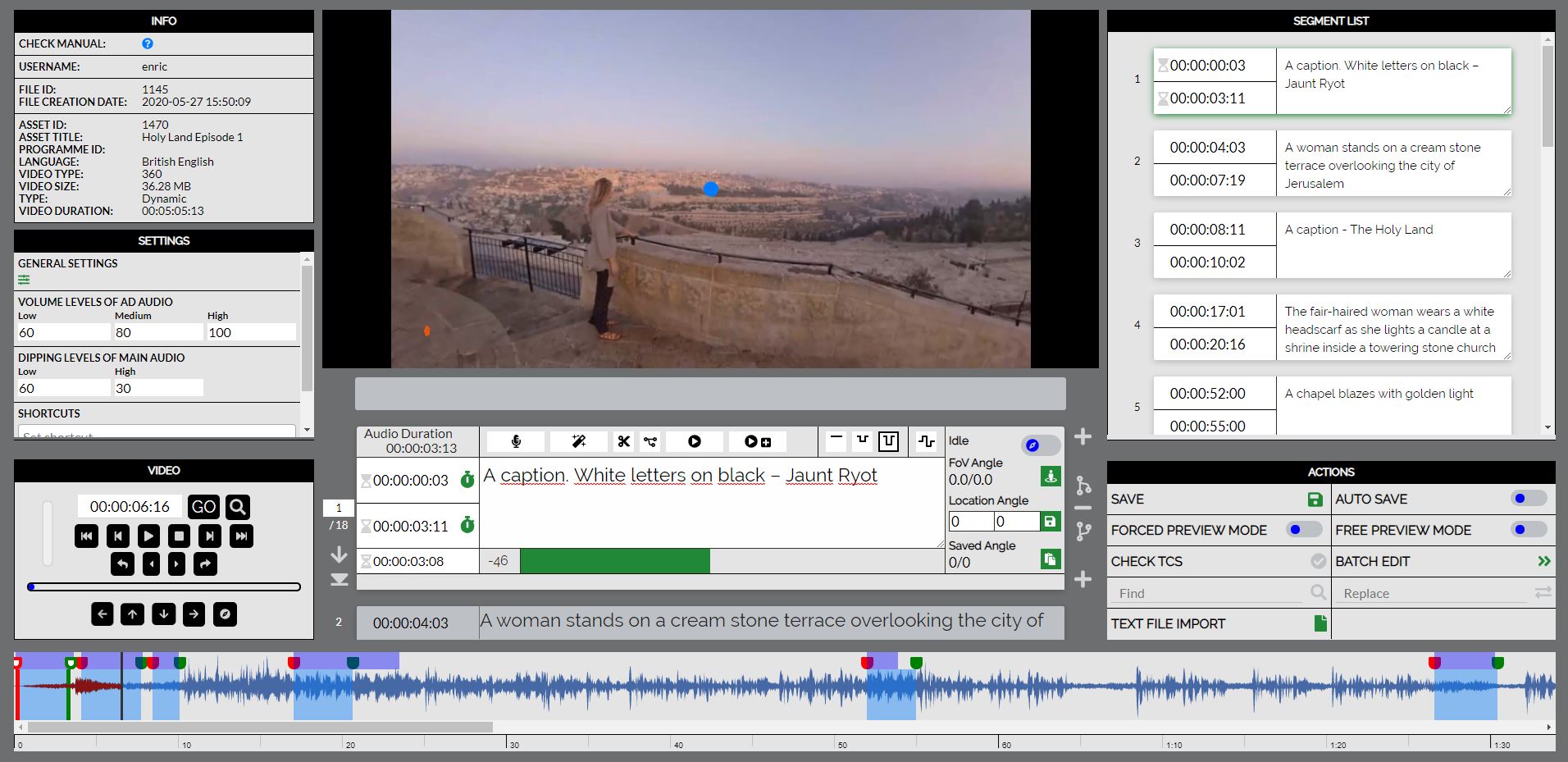
- Multi-language interface
- Standard and user-configurable shortcut keys for most commonly used operations of the editor
- User and file settings (layout, preferences, languages, character configurations, region configurations, minimum values, default values, etc.). Setting profiles can be created for different programmes such as films, series, documentaries, etc. The setting profiles can be shared among producers
- Script edition in the same editor with segment metadata (time codes, main audio dipping, etc.)
- A text file can be imported to be used as AD script
- Segment audio either generated automatically with Voice Synthesis of the segment script or recorded from the microphone connected to the computer by reading the segment script
- Segment audio edition tools (cut, split, short/long test, etc.)
- Special audio description segment tools required by professional users such as batch edition
- Compatible with 2D and 360º (immersive) videos
- Integrity check for warnings and errors on quality constrictions
-
Graphical aids such as thermometers, timeline with audio waveform and segment tools
- Preview modes for final verification purposes
- Audio description segments (audio files and metadata) are stored in a single compressed file allowing an improved exchange between platforms
Documentation:
The Web AD Editor is a cloud-based editor to create/edit sign language files for TV and online media with a user-friendly interface and graphical video soundwave in time. This module is totally integrated with the ACM.
Main features:
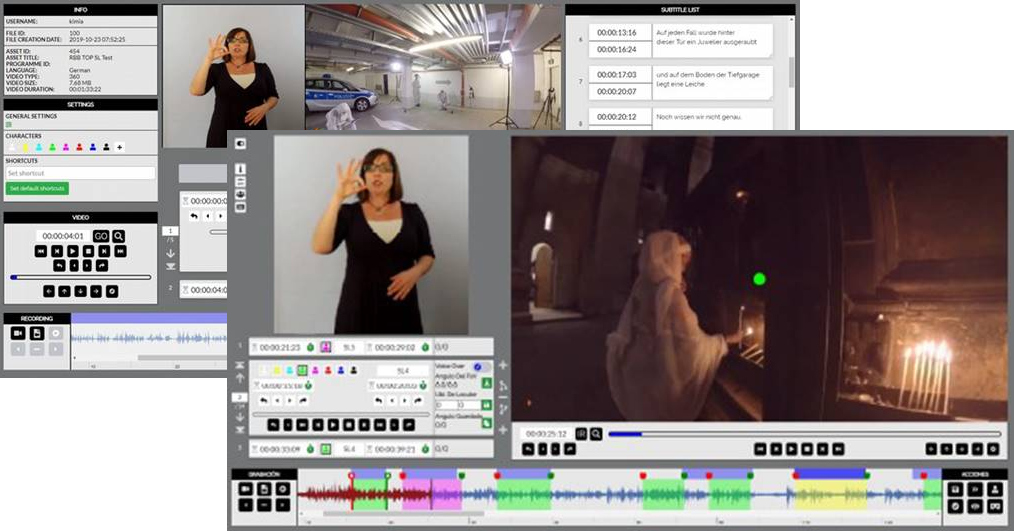
- Two working environments based on user preferences: Classic layout and Compact layout
- Multi-language interface
- Standard and user-configurable shortcut keys for most commonly used operations of the editor
- User and file settings (layout, preferences, languages, character configurations, region configurations, minimum values, default values, etc.). Setting profiles can be created for different programmes such as
films, series, documentaries, etc. The setting profiles can be shared among producers - Interpreter video either recorded from camera connected to the computer or from video file being imported
- Subtitles for the deaf or hard of hearing sign language interpreters during the interpreter recording
- Special sign language segment tools required by professional users such as batch edition
- Compatible with 2D and 360º (immersive) videos
- Integrity check for warnings and errors on quality constrictions
-
Graphical aids such as thermometers, timeline with audio waveform and segment tools
- Preview modes for final verification purposes
- Sign language segments (video files and metadata such as time codes and character information) are stored in a single compressed file allowing a better exchange between platforms
Documentation:
Different stakeholders will benefit from the use of the Online Editors such as:
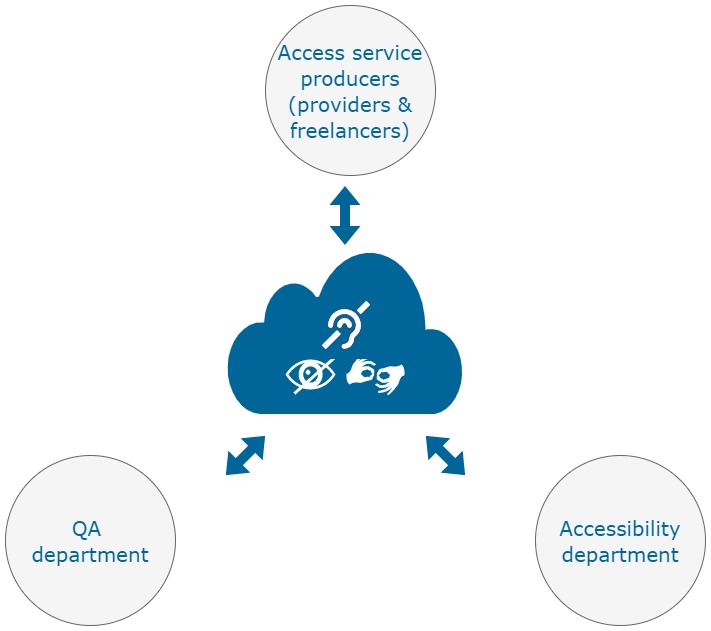
- Access service producers (service providers and freelancers), make usage of the Online Editors via the ED interface of the ACM to produce and edit the access service files (subtitle, audio description and sign language) on a fully cloud-based environment
- QA department makes usage of the Online Editors via the CM interface of the ACM to verify the access service files
- Accessibility department makes usage of the Online Editors via the CM interface of the ACM to preview the access service files
|
|
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 761974. |

